Against a Backdrop of Bird Declines, Complex Problems Meet Creative Solutions
By Lynn Scarlett
May 4, 2023In the face of decades of population declines, recent successes highlight how conservation depends on broad collaborations, novel partnerships, and the magic of human nature.
This Perspective essay appears in the Autumn 2023 issue of Living Bird magazine. Subscribe now.
Over the past century, declines in populations of iconic birds—beautifully feathered waders in Florida, California Condors, Bald Eagles—have occasionally made headlines and spurred conservation actions. In September 2019, the perils faced by birds once again made headlines. This time, the news was dramatic and comprehensive. A study published in the journal Science declared North America had lost 3 billion birds since 1970—losses encompassing hundreds of species in grasslands, forests, along shores, all across the continent.
Media pronouncements about the study, led by scientist Ken Rosenberg of the Cornell Lab of Ornithology and others, sounded the alarm: Was a century of conservation failing? Was there still hope?
Reflecting on these questions, journalists Anders and Beverly Gyllenhaal spent a year interviewing scientists, technology experts, conservation entrepreneurs, and federal agency leaders for their new book A Wing and a Prayer: The Race to Save Our Vanishing Birds, released by Simon & Schuster in April. In their conversation with Cornell Lab executive director emeritus John W. Fitzpatrick, he opined the challenge can best be summed up as “not rocket science.”
“It’s vastly more complicated than rocket science,” Fitzpatrick said.
As the Gyllenhaals reveal, the science required to understand the extent of bird population declines over the past 50 years is, itself, enormously complex—involving ecology, ornithology, biostatistics, computer science, acoustic engineering, genomics, satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, and nanotechnology. Also complex are the threats to birds, which encompass loss of habitat, climate change, pesticides, invasive species, diminishing water supplies, and ravages on bird populations by outdoor domestic cats.
These threats stretch from the Arctic to the tip of South America. They play out at the interface of people and places—and therein lies the most complicated challenge. Over the past century, land management reveals a saga of tensions between natural ecosystems and human hands on landscapes.


A Front-Row Seat
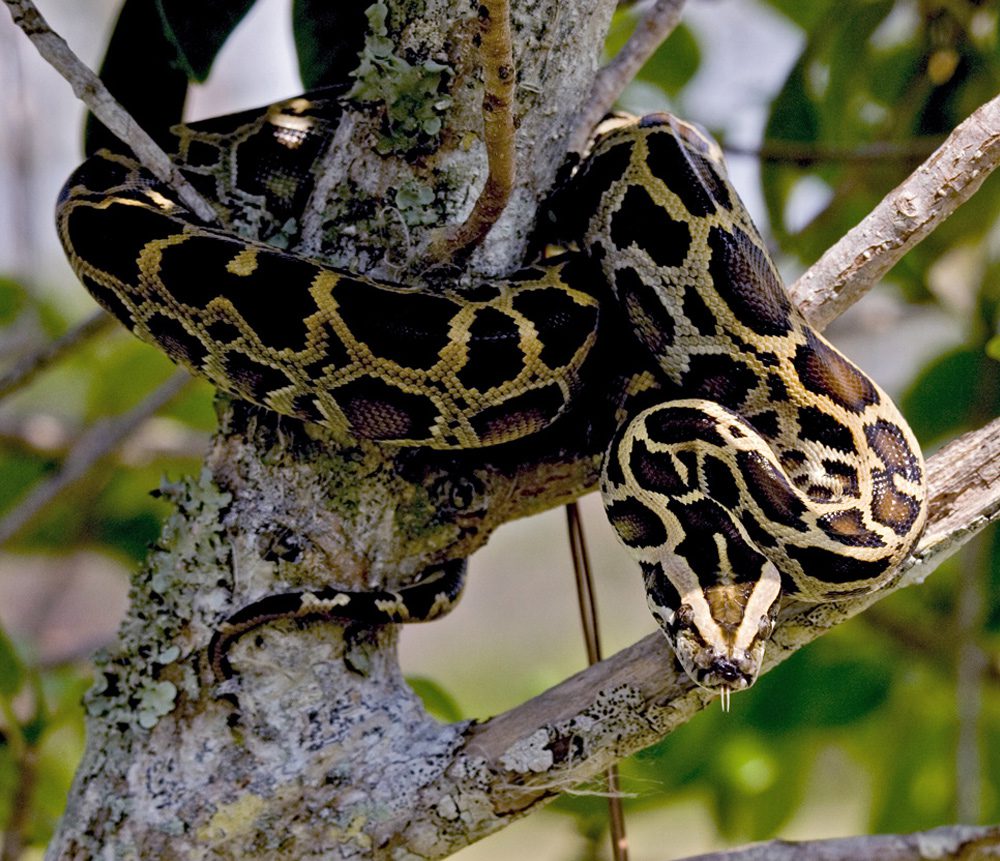
I had a front-row seat to these complexities during my eight years at the U.S. Department of the Interior from 2001 to 2009, and another eight years at The Nature Conservancy from 2013 to 2021. In Hawaii, I held the beautiful Iiwi, a scarlet honeycreeper threatened by loss of forest habitat and avian diseases. On the Channel Islands off the coast of Santa Barbara, I learned about how invasive rats had decimated cliff-nesting seabirds. In Guam, I found that brown tree snakes had nearly annihilated bird populations, resulting in an eerie dawn silence. Deforestation, hunting, pesticides, and other human actions brought populations of the Puerto Rican Parrot to a low of 13 birds in the 1970s, prompting a captive breeding program. On Midway Island, Laysan Albatross chicks died when fed, inadvertently, plastic wastes brought to them by their parents. I traipsed through deep, salt-tolerant grasses in the Everglades, where I came upon a 9-foot python—one of the tens of thousands that are decimating bird and mammal populations. All across America, I saw birds devastated by oil spills, imperiled by wind turbines, and stricken by pesticides.
Sometimes people, even public agencies, simply circumvent legal requirements or strive to eliminate them, as in the 2017 bold move by appointed Department of the Interior officials under the previous Presidential administration to reinterpret the 100-year old Migratory Bird Treaty Act. The Act is emphatic: “unless and except as permitted…it shall be unlawful at any time, by any means or in any manner, to pursue, hunt, take, capture, kill…any migratory bird….” Despite the clarity of this language, the Interior Department officials abruptly shifted course, narrowing interpretation of the Act to apply only when killing or “taking” birds is the purpose of the action rather than an incidental side effect of, say, logging or energy production. Ultimately, the effort to reinterpret the Act failed, but this episode illustrates the persistent vulnerability of conservation to changes in laws and regulations.
But even efforts focused on conservation present challenges for bird protection. As Fitzpatrick tells the Gyllenhaals, what becomes evident is: “We’re not going to find a master solution.” It is not always clear what can even be done, for example, to eliminate invasive pythons or brown tree snakes. In other cases, there may be trade-offs: as in the choice between maintaining drier nesting areas for Cape Sable Seaside Sparrows in the Everglades or maximizing wetland restoration. Sometimes costs are high—$5 million per year for the California Condor—and available resources are scarce, so some species go unattended. Sometimes focus on a single species like the Greater Sage-Grouse may result in practices ideal for it, but not for other sagebrush habitat birds.


Making Conservation Collaborative
Science can help sort out some of these challenges. But sometimes conservation actions provoke deep tensions with economic or other interests. Sarah Sawyer, who oversees California Spotted Owl conservation for the U.S. Forest Service, describes to the Gyllenhaals a “cautionary tale” in the history of protecting the Northern Spotted Owl, a trajectory in which owl protection collided with the local timber industry. The Gyllenhaals sum up the experience as a “roiling mix of politics, science, violence, and sabotage.”
Drawing on her experiences in Africa doing fieldwork in places where local communities relied on logging or other natural resources for their livelihoods and survival, Sawyer concludes that enduring conservation requires engaging everyone—recreationists, those whose livelihoods are tied to using land and water resources, environmental advocates, and others. The need to transcend natural resource “battles,” combined with growing recognition of a need for landscape-scale action, have inspired collaborative conservation in which communities are coalescing in partnered problem solving.
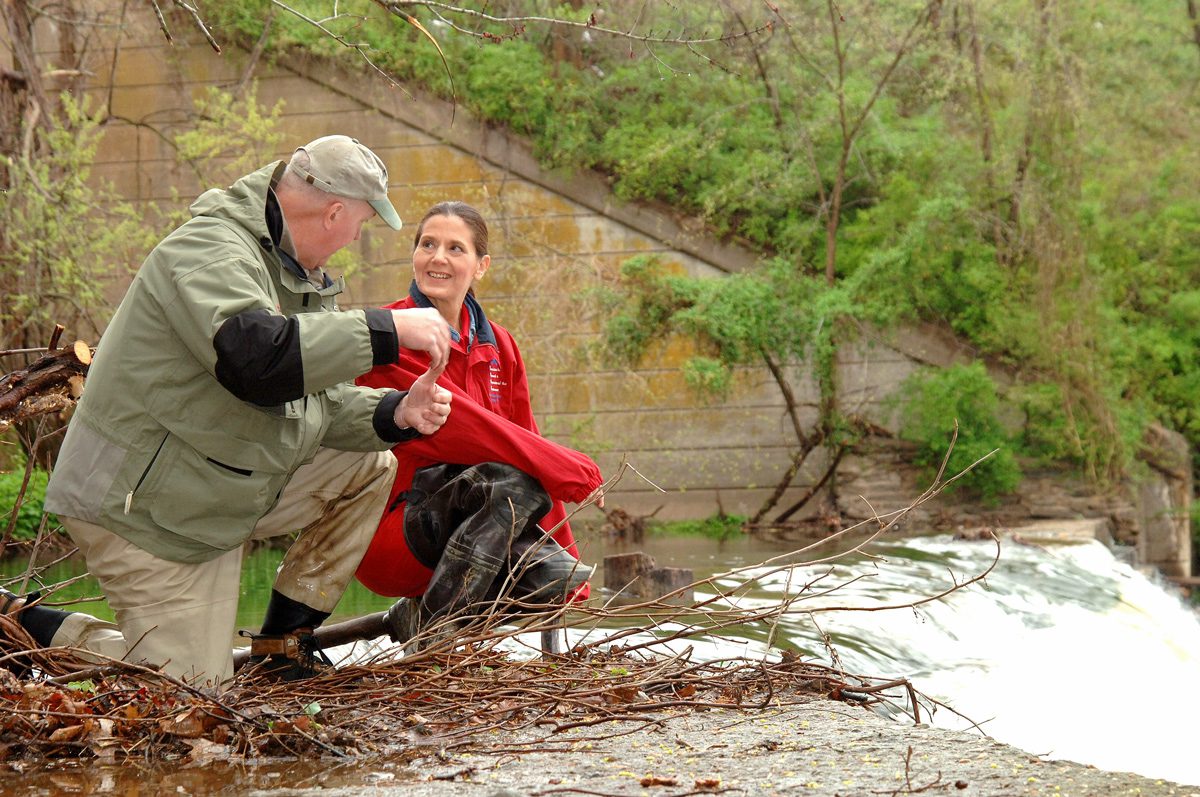

I remember a trip while I was Deputy Secretary at the Interior Department to western Pennsylvania at Buffalo Creek. There, dozens of farmers, partnering with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and a local university, are fencing off miles of streams and riparian areas. They are planting native warm spring grasses. They are installing owl and Wood Duck boxes. The result is dramatic reductions of bacteria in water, which is good for nature, the dairy cows at Buffalo Creek, and the farmers that tend them. Streambanks now display dense shrubs, bringing habitat for birds and shade cover for fish.
I have met ranchers and farmers across the continent shifting to regenerative agriculture to restore soil health, maintain native grasses, and enhance stream flows, affirming conservation pioneer Aldo Leopold’s vision of linking conservation with sustaining livelihoods. Reversing trends in declining bird populations must include these endeavors of collaborative action and the power of each individual to make a difference.
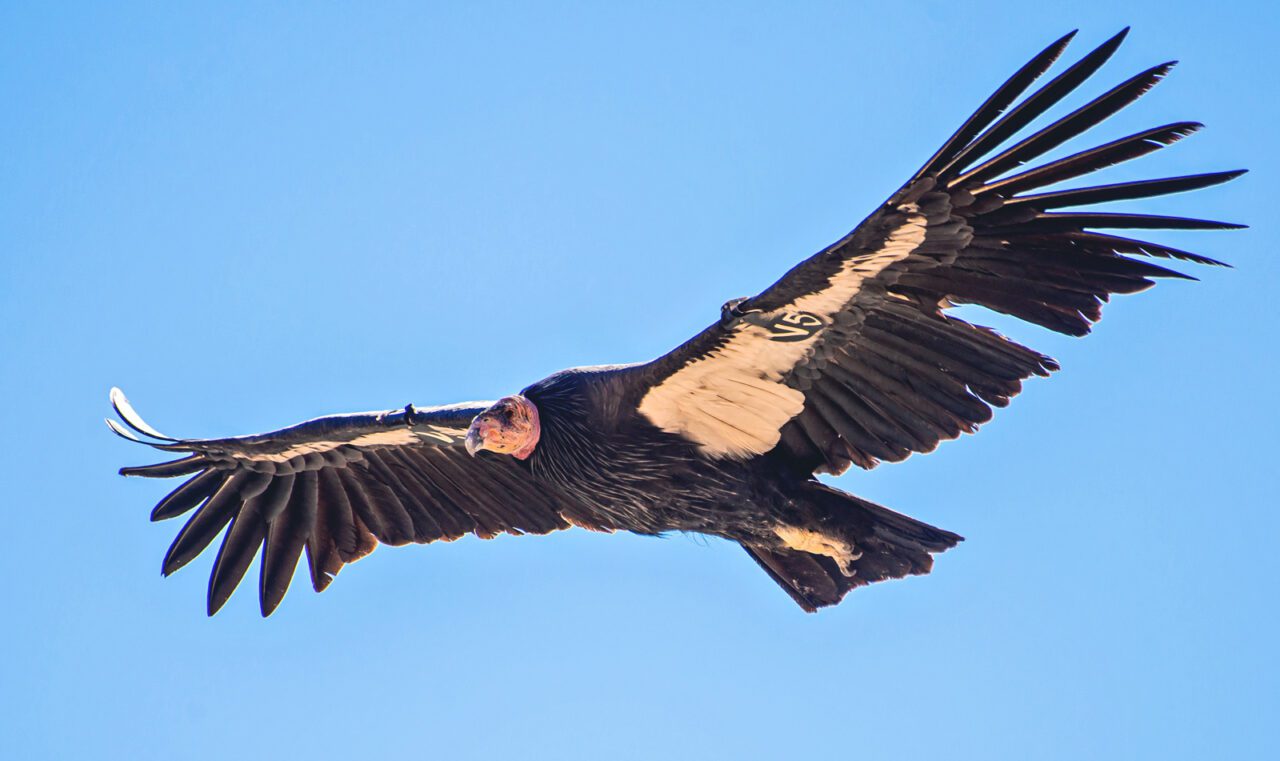

Learning from the Condor’s Return
Some years ago, I listened to an Indigenous Athabaskan leader recall a time of his ancestors when the California Condor soared skies all the way to Canada. Over 25 years ago, hiking in the San Rafael Wilderness in California, I heard a haunting whistle. I looked up and saw six condors—recently released from a captive breeding program—soaring overhead. At the time, just 15 condors had been set free into the wild. Over a decade ago, I held a California Condor in my arms—assisted by two USFWS employees, one who held the beak and one the legs. Together, we opened our arms and released this bird into the wild.
A year or so later, I returned to the wild lands beyond Ojai, California, with a close friend and one of my heroes, John Ogden. Over 35 years ago, John, a scientist, led the team that scaled cliffs and hiked mountains to retrieve from the wild the last remaining California Condors and bring them into captivity to breed them with the hopes of rebuilding a condor population to return to the wild. I stood with John, 25 years after he had set forth to save the condor amid much controversy, even death threats. Yet John and his colleagues had persisted.
We stood shoulder to shoulder watching the fruits of that labor as 12 condors soared overhead and, at dusk, glided in to roost upon snags where once their ancestors had presided. Today, ranchers have joined the efforts to sustain this bird. The story of the condor is a broader metaphor for the better angels of ourselves. Though the details vary, species by species, the future of birds perhaps resides in what Cuban biologist Giraldo Alayón, contemplating protection of the Ivory-billed Woodpecker, once referred to as that space “between science and magic.”
The science can guide us; the magic resides in the conservation commitment of each of us.

All About Birds
is a free resource
Available for everyone,
funded by donors like you
American Kestrel by Blair Dudeck / Macaulay Library